The Practical Way to Decarbonize at Industrial Scale
H2Gen® converts water to pure hydrogen by using residual electrochemical energy in various industrial off gases and biogenic gases to drive water electrolysis without electricity, and concentrates carbon dioxide in off gases as a separate product stream enabling economic industrial decarbonization.
H2Gen® Reactor Design and Scale Up
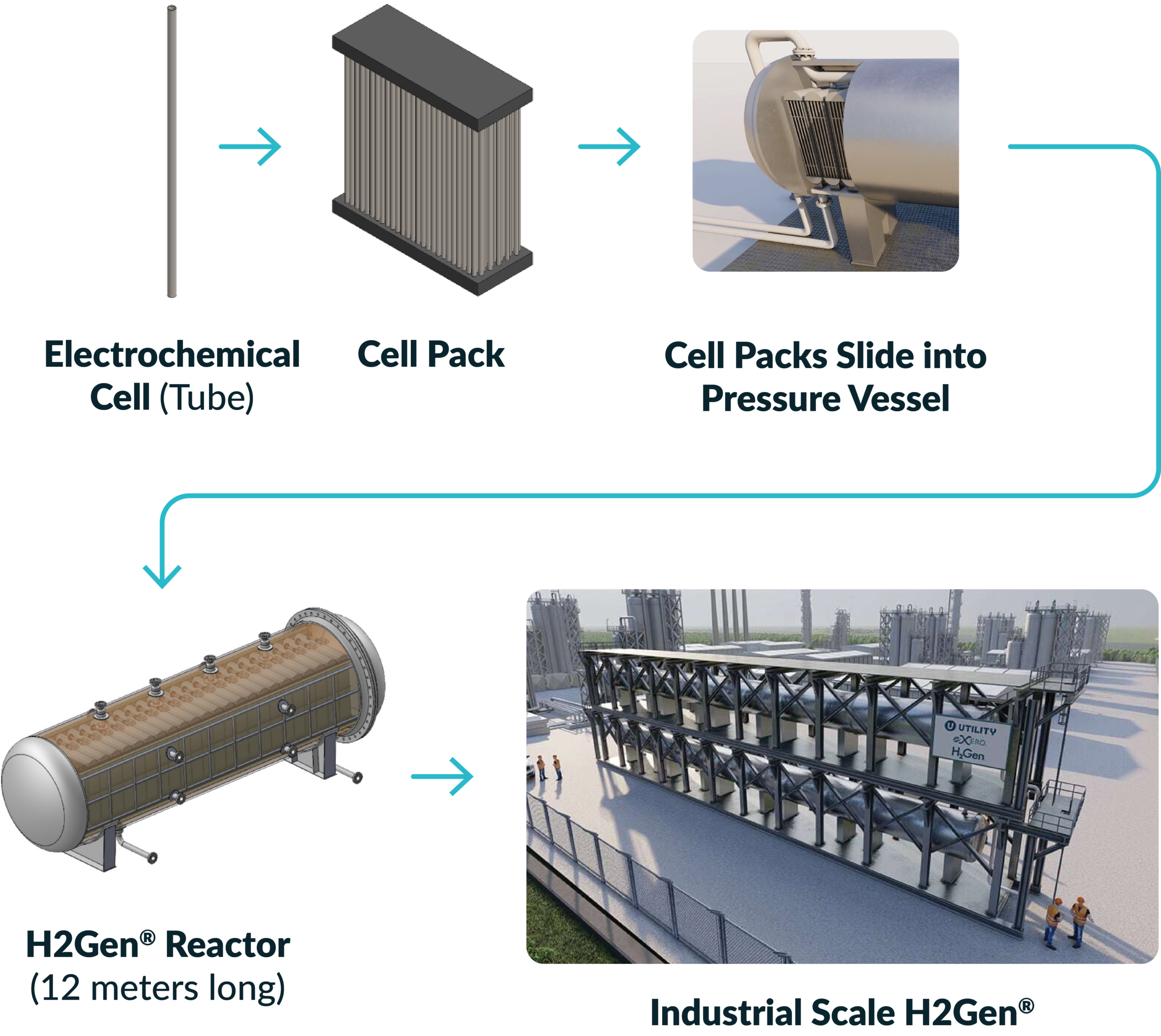
How H2Gen® Works
H2Gen® has just two inputs, water and feed gas. The H2Gen® feed gases including industrial off gases or biogenic gases. Natural gas is not required as feed gas but if desired by customers and partners, it can be used as well. All hydrocarbons in the feed gases are cracked to syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen, before entering H2Gen®.
H2Gen® converts water in its vapor phase into pure hydrogen by using residual electrochemical energy in industrial process off gases or biogenic gases to drive the water electrolysis reaction without electricity.
H2Gen® also concentrates carbon dioxide in feed gases to high purity as a separate product stream (often exceeding 95% CO2 purity in some applications), making it ready for a single-point carbon capture at a significantly reduced cost and footprint.
This combination of H2Gen® products, pure hydrogen and high purity CO2, offers the most economical commercially available solution for rapidly decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors at any scale,including steel, refining, petrochemicals, chemicals, low-carbon fuels, and upstream oil & gas.
The H2Gen® Breakthrough
The first H2Gen® breakthrough removes external power requirement for the water/steam reducing reaction, that is, splitting H2O into pure hydrogen and oxygen ions on the cathode side of Utility’stubular electrochemical cell, which is the heart of the H2Gen® technology. Due to concentration difference, the oxygen ions (O2-) move from the cathode side (i.e., inside the tube where steam flows) across the proprietary gas-tight electrolyte to the anode side (i.e., outside the tube) where off gases are oxidized to carbon dioxide or water (e.g., CO to CO2 or H2 to H2O).
The oxidation reaction on the anode side releases two electrons (2e–) that move through the same proprietary gas-tight electrolyte to the cathode side where they electrolyze/reduce new H2O molecules into pure hydrogen and oxygen ions. The electrons move this way due to a naturally occurring electrochemical potential difference between the off gases and steam. This potential difference (i.e., voltage) is captured by the foundational Nernst Equation.
Steam (H₂O) approaches the cathode side while carbon monoxide (CO) approaches the anode side to spontaneously initiate the electrochemical reaction to reduce water to hydrogen (H₂).
H₂ and CO₂ molecules detach from the cathode and anode to free up the surface area for new H₂O and CO molecules to come to the surface and repeat the reaction.
This cycle repeats as long as the flow of steam and off gases continues. Utility’s proprietary electrolyte, which conducts both oxygen ions and electrons, represents the second breakthrough enabling H2Gen® technology. Materials with this capability are commonly referred to as Mixed Ionic Electronic Conductors (MIEC). Click Here to find out more in this article published by Oak Ridge National Laboratory (UT-Battelle for Department of Energy)
By combining these technological breakthroughs with deep expertise across multiple engineering and scientific disciplines, Utility has made H2Gen® both possible and commercially available, fundamentally transforming how businesses and policy makers’ approach decarbonizing hard–to–abate sectors.
Utility is a global leader in economic industrial decarbonization, enabled by its proprietary electrochemical cell technology that operates without external electrical power.
Built on many years of innovation and deep expertise in electrolytic membranes, electrochemical module design, gas-conversion building blocks, and full system integration, Utility has established a robust and differentiated intellectual property foundation. Our growing global patent portfolio (29 granted, 84 pending) spans across core materials, platform extensions, multiple industrial applications, and continuous process and design advancements, providing strong protection for our products and technologies.
Utility’s worldwide patent and trademark portfolio is broad, active, and continuously expanding, reinforcing our long-term technology leadership and competitive advantage.
H2Gen® Technology Highlights
Electrochemical cells operate as independent reactors that scale seamlessly from small installations to large-scale industrial systems. Modular, small footprint, factory-built design enables phased deployment, rapid expansion, and configurations tailored to site-specific needs.

In a single-step process, H2 is made from H2O without electricity or natural gas. Water purification requirement is less compared to electrolysis. H2 is not separated from other gases compared to SMR (Steam Methane Reforming). CO2 is concentrated without a dedicated carbon capture plant. These and other process advantages drive down the capital and operating costs of H2Gen®.

Without the need for fossil-based feedstocks such as natural gas, H2Gen® utilizes industrial off gases and biogenic feedstocks, substantially reducing the carbon footprint of facilities and end-products, and reliance on the complexities of natural gas supply and pipeline connections.
Conventional industrial processes rely on catalysts to improve equilibrium-limited chemical reactions. H2Gen® works differently; it drives an electrochemical reaction between the anode and cathode verses a chemical equilibrium reaction, eliminating the need and cost of catalysts altogether.

Generates a highly concentrated CO₂ stream (up to ~95% purity) as part of the process, significantly reducing the cost, complexity, and footprint of CCUS. This enables more efficient, practical and economical utilization or sequestration pathways.

Validated through successful field demonstrations and announced commercial projects, utilizing steel off gases and syngas as the feed. Designed to operate reliably within active industrial facilities under real-worldprocess conditions and operational requirements using a wide range of industrial feed gases.

Achieving clean H2 costs below grey H2 in many applications with a separate and free concentrated CO2 stream, H2Gen® enables a wide range of decarbonized end-products.
Universal H2Gen® Reactor for All Applications
Single-Reactor Plants: 2 – 5 TPD
Ideal for biogas projects, hydrogen mobility applications, using one or two reactors to produce clean hydrogen economically.
Multiple–Reactor Train Configurations 50-500 TPD
Ideal for Steel or Refining projects where multiple reactors are connected into trains (e.g., five in-line connected reactors that can be stacked on top of each other) to achieve large plant capacities, maintaining a record small footprint and competitive costs.